Protein Synthesis
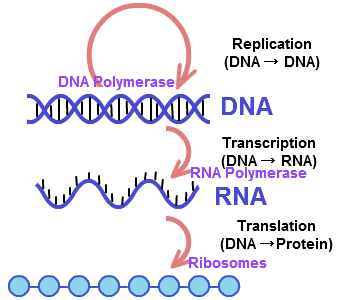
Transcription
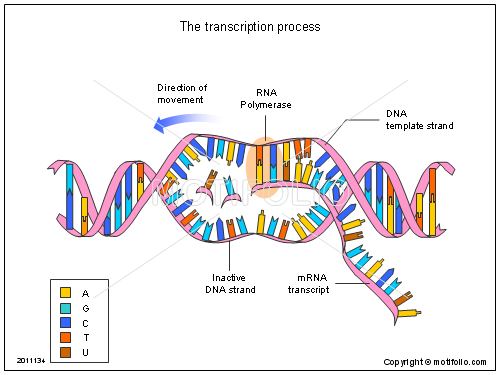
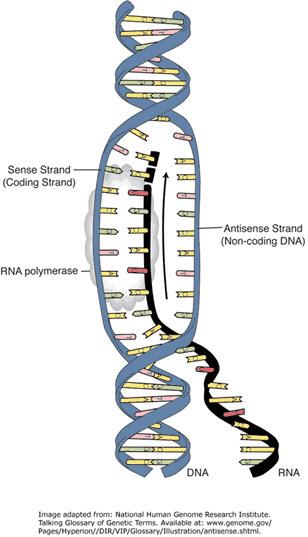
Transcription is When DNA is changed into RNA.
Step 1
DNA unwinds
Step 2
One side of DNA "codes for a protein"
mRNA is "transcribed" from DNA by complementary base pairing (mRNA has no thymine, which is replaced by uracil)
Step 3
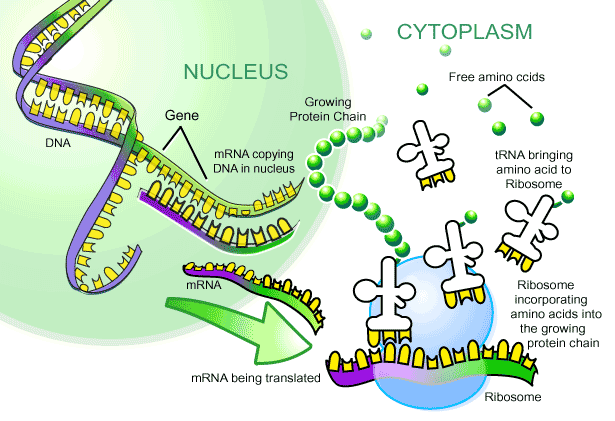
mRNA passes out of the cytoplasm to the ribosome
Translation
Step 1 of Translation mRNA attaches to the ribosome.
Step 2 of Translation
tRNA's attach to free amino acids in the cytoplasmic "pool" of amino acids.
Step 3 of Translation
Protein chain continues to grow as each tRNA brings in its amino acid and adds it to the chain.
Translation is when RNA is being changed into a Protein.
Trna is the bringing of the Amino Acids into the Ribosome.
Mrna Molecules carry the message from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
Rrna decodes the codon.
Transcription is When DNA is changed into RNA.
Step 1
DNA unwinds
Step 2
One side of DNA "codes for a protein"
mRNA is "transcribed" from DNA by complementary base pairing (mRNA has no thymine, which is replaced by uracil)
Step 3
mRNA passes out of the cytoplasm to the ribosome
Translation
Step 1 of Translation mRNA attaches to the ribosome.
Step 2 of Translation
tRNA's attach to free amino acids in the cytoplasmic "pool" of amino acids.
Step 3 of Translation
Protein chain continues to grow as each tRNA brings in its amino acid and adds it to the chain.
Translation is when RNA is being changed into a Protein.
Trna is the bringing of the Amino Acids into the Ribosome.
Mrna Molecules carry the message from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
Rrna decodes the codon.